KPMG's second edition of the 'Infrastructure 100: World Cities Edition', showcases 100 of the most innovative and inspiring urban infrastructure projects from around the world.
This study provides insight into the innovations that make them 'Cities of the Future' - places where people want to live and do business, says KPMG.
The aim of Infrastructure100 is to showcase and celebrate one hundred examples of great projects underway in cities around the world.
Of the 100 projects, 10 were selected by a global judging panel as being the most noteworthy within each project category.
This study provides insight into the innovations that make them 'Cities of the Future' - places where people want to live and do business, says KPMG.
The aim of Infrastructure100 is to showcase and celebrate one hundred examples of great projects underway in cities around the world.
Of the 100 projects, 10 were selected by a global judging panel as being the most noteworthy within each project category.
1. Urban Mobility: East Side Access, New York City, United States of America
2. Global Connectivity: Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor, Delhi to Mumbai, India
 The $90 billion project will stretch across seven states and link the nation's capital, Delhi, with the financial capital, Mumbai.
The $90 billion project will stretch across seven states and link the nation's capital, Delhi, with the financial capital, Mumbai.The sheer scale and far-reaching impact of the project impressed the judges with plans including a high-speed rail line for freight, a six-lane expressway and a 4,000 megawatt power station.
The idea is to develop centres of industrial production along the length of the corridor. The project plan includes nine industrial zones and 24 new cities.
3. Urban Regeneration: Oresund Regional Development, Denmark and Sweden
The Oresund Regional Development project creates a cross-border economic zone between Sweden and Denmark, focused on Malmo and Copenhagen.
The two cities are connected by an impressive new international crossing and share a considerable amount of physical infrastructure.
The aim is to continue to foster growth and connectivity via the proposed 18 kilometer Fehmarnbelt Tunnel, which will bring Germany and Scandinavia closer together.
The aim is to continue to foster growth and connectivity via the proposed 18 kilometer Fehmarnbelt Tunnel, which will bring Germany and Scandinavia closer together.

4. Education: Princess Nora Bint Abdul Rahman University for Women, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Princess Nora Bint Abdul Rahman University for Women was widely lauded by the judges and is considered a major step in obtaining equal access to education for women in the Middle East.
The self-contained campus will cover 8 million square meters just outside Riyadh and accommodate 40,000 students.
The self-contained campus will cover 8 million square meters just outside Riyadh and accommodate 40,000 students.
The university will have the capacity to accommodate 60 per cent of the city's high-school graduates and will offer degrees in medicine, pharmacy, management and IT.
According to the judges, the project has a "generational theme" and its effect will ripple across the whole country for years to come.
According to the judges, the project has a "generational theme" and its effect will ripple across the whole country for years to come.
5. Healthcare: Royal London Hospital, London, UK
The Royal London Hospital at White chapel in the United Kingdom is one of the oldest operating healthcare facilities in England.
The Victorian-era hospital – often associated with the grittiness of the capital's East End – was redeveloped and funded through a 1.1 billion pound PFI.
Following its redevelopment, the new hospital reopened its doors in March 2012 and is now one of Britain's largest, most advanced healthcare facilities.
The new hospital has 1,248 beds, an increase of 186 on the previous facility, with over 40 percent in single rooms with en suite facilities.
Wards are light and airy with natural ventilation and separate areas for women and men, and the 22 operating theaters are one-third larger than their predecessors.
6. Water: Tuas II Desalination Plant, Tuas, Singapore
In Singapore, the Tuas II Desalination Plant will serve a vital function, delivering 318,500 cubic meters (70 million gallons) of water per day for a 25-year concession period from 2013 to 2038.
Singapore currently relies on rainfall and imports from neighboring Malaysia for freshwater supplies.
The wealthy city-state has made several investments in recent years to become more independent and meet the needs of an increasing population.
7. New and Extended Cities: Tianjin Eco City, Tianjin, China
In the Far East, judges were impressed with Tianjin Eco-city being developed with "practical" technology on challenging arid terrain in northern China.
The city is an ambitious economic collaboration between China and Singapore to pilot a more liveable alternative to some of the country's polluted megacities.
With an advanced light rail system, solar energy and smart grid technology, Tianjin eco-city is set to create a new benchmark among global cities.
8. Recycling and Waste Management: Deep Tunnel Sewerage System, Kranji to Changi, Singapore
The Deep Tunnel Sewerage System in Singapore has been under construction since 2000 and is scheduled for completion in 2020.
The massive scheme has been designed to address all of the city-state's long-term needs for used water collection, treatment, reclamation and disposal.
The award-winning system works entirely by gravity, thus eliminating the need for pumping stations and the risks of used water overflows as well.
9. Urban Energy Infrastructure: Cidade Inteligente, Buzios, Brazil
Brazil is at the forefront of intelligent energy systems with its impressive Cidade Inteligente Buzios project.
Among the benefits for consumers are the possibilities of having discounted energy prices dependent on time of usage, consumption control of household appliances, energy savings through the installation of new LED street lighting and increased energy efficiency in public buildings.
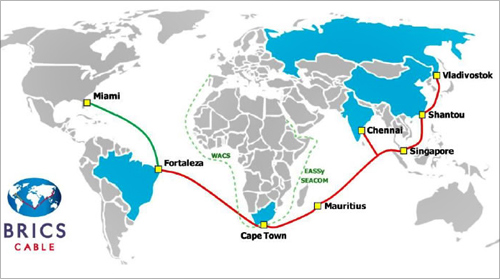
10. Communications Infrastructure: BRICS Cable Project, South Africa and Mauritius
A hugely ambitious initiative designed to boost international communication between cities and global access to high-speed internet is the BRICS Cable Project.
As the acronym suggests, this initiative aims to connect the BRIC markets and the United States with a 34,000 kilometre two-fiber pair submarine cable with capacity of 12.8Tbit/s via cities like Jacksonville (USA), Fortaleza (Brazil), Cape Town (South Africa), Port Louis (Mauritius), Chennai (India), Singapore, Shantou (China) and Vladivostok (Russia).
With enhanced internet connectivity, the cable would boost trade links and economic competitiveness.